

What are Semiconductors ?
Materials such as paper, wood, resin, etc. that block electricity are called "insulators", by contraries, those materials that conduct electricity such as copper wires/steel are called "conductors". "Semiconductors" are neither of the two and can be insulators or conductors depending on the given conditions.
The main semiconductor materials are silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge). In
the periodical table of the elements they fall under the column of carbon
(C). Silicon is found in sand as SiO2 and, therefore, abundantly available
throughout the globe. However, silicon cannot be used as semiconductors
as is. It is necessary to transform it into single-crystal carbon like
that of diamonds. It looks like the process of manufacturing is not easy.
1 H
hydrogen |
|
2 He
helium |
3 Li
lithium |
4 Be
beryllium |
|
5 B
boron |
6 C
carbon |
7 N
nitrogen |
8 O
oxygen |
9 F
fluorine |
10 Ne
neon |
11 Na
sodium |
12 Mg
magnesium |
|
13 Al
aluminium |
14 Si
silicon |
15 P
phosphorus |
16 S
sulphur |
17 Cl
chlorine |
18 Ar
argon |
19 K
potassium |
20 Ca
calcium |
21 Sc
scandium |
22 Ti
titanium |
23 V
vanadium |
24 Cr
chromium |
25 Mn
manganese |
26 Fe
iron |
27 Co
cabalt |
28 Ni
nickel |
29 Cu
copper |
30 Zn
zinc |
31 Ga
gallimu |
32 Ge
germanium |
33 As
arsenic |
34 Se
selenium |
35 Br
bromine |
36 Kr
krypton |
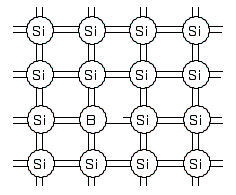
The atomic structure of silicon consists of a central nucleus surrounded by 2 electrons in the first orbit (K-shell), 8 electrons in the second orbit (L-shell), and 4 electrons in the third orbit (M-shell).
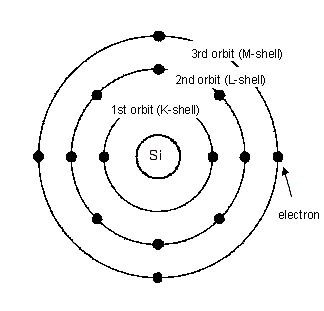
The 4 electrons in the outermost shell are called the valence electrons.
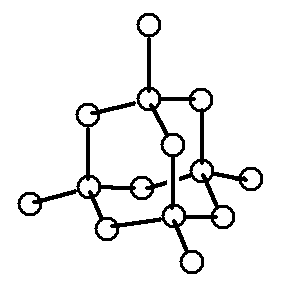
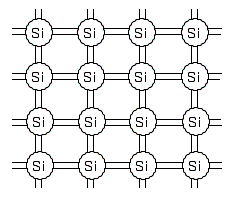
In a high-purity silicon crystal, each atom shares its 4 electrons with the neighboring atoms, and this sharing is called covalent bonding. Silicon is not electrically conductive because all of its electrons are bound and do not move freely.
N-type semiconductor
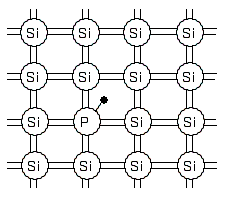
If a trace amount of an element with 5 electrons in the outermost shell (such as phosphorous) is added to the crystal, the excess valence electrons gained can move freely through the crystal, making it electrically conductive.
P-type semiconductor
If a trace amount of an element with 3 electrons in the outermost shell (such as boron) is added to the crystal, we obtain an electron deficiency called a hole. These holes behave like electrons, and the crystal becomes electrically conductive.
Total(1997)  Today
Today  Yesterday
Yesterday 
|






